The IMode Interface
The IMode interface is similar to the IBlockCipher
interface, except modes have a state associated with them, e.g.
whether the instance is used for encryption or decryption. The
IMode interface is usually the one that is used when encrypting
or decrypting; IBlockCipher is used when the lowest level--the
cipher function itself--needs to be accessed. IMode extends
IBlockCipher interface, and thus all methods specified in that
interface are implemented in modes, and have the same meaning. The
properties passed to the init method of IBlockCipher may
also be passed to the init mehtod of IMode, along with the
following property names.
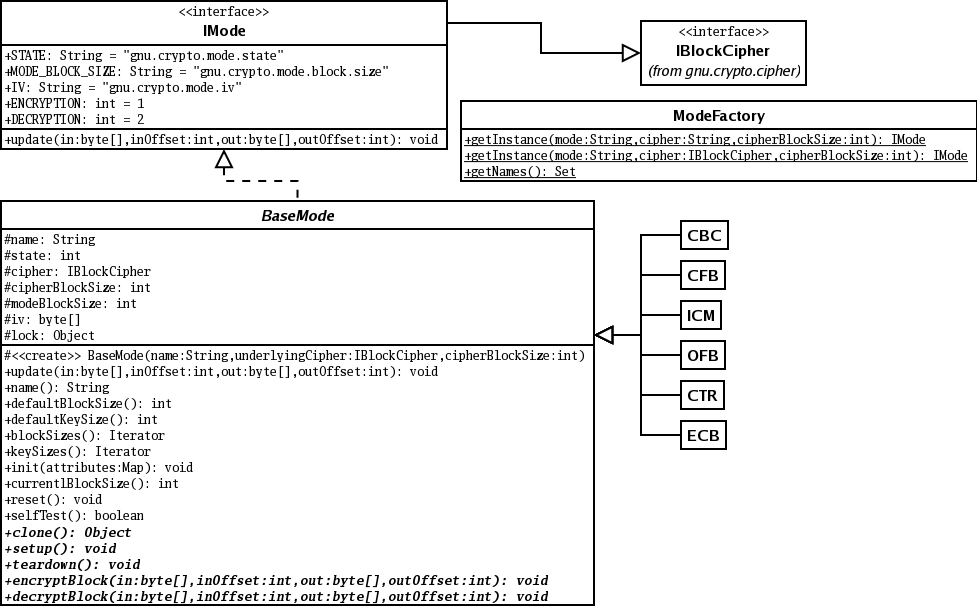
Figure 2: Modes class diagram
| java.lang.String STATE
|
Variable |
The property name for the mode's state, as passed to the init
method. Values for this property are an java.lang.Integer
containing either the ENCRYPTION constant or the
DECRYPTION constant.
|
The value passed for the STATE property, wrapped in a
java.lang.Integer, which indicates that the instance is to be
used for encryption.
|
The value passed for the STATE property, wrapped in a
java.lang.Integer, which indicates that the instance is to be
used for decryption.
|
| java.lang.String MODE_BLOCK_SIZE
|
Variable |
The property name for the block size of this mode. The value for this
propery should be a java.lang.Integer of the block size. If
omitted, the underlying cipher's block size is used.
|
| java.lang.String IV
|
Variable |
The property name for the initialization vector to initialize this mode
with, if required. The value should be a byte array equal in size to the
MODE_BLOCK_SIZE property. If omitted a byte array consisting of
zeros is used.
|
| void update (byte[] in, int inOffset, byte[] out, int outOffset) throws java.lang.IllegalStateException
|
Function |
Transforms the block in in starting at inOffset into the
block in out starting at outOffset. Encryption or decryption
is performed depending upon the value passed along with the state
property given to the init method. A
java.lang.IllegalStateException is thrown if this instance has
not been initialized, and it is up to the programmer to ensure that
there is one full block in in starting at inOffset, and
enough space for one full block in out starting at
outOffset. Since modes can have states, and may require that the
be used in a particular sequence, using this method is preferred over
the encryptBlock and decryptBlock methods of
IBlockCipher.
|
