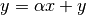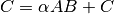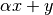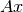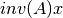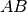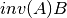BLAS Support¶
The Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms (BLAS) define a set of fundamental operations on vectors and matrices which can be used to create optimized higher-level linear algebra functionality.
The library provides a low-level layer which corresponds directly to the
C-language BLAS standard, referred to here as “CBLAS”, and a
higher-level interface for operations on GSL vectors and matrices.
Users who are interested in simple operations on GSL vector and matrix
objects should use the high-level layer described
in this chapter. The functions are declared in the file
gsl_blas.h and should satisfy the needs of most users.
Note that GSL matrices are implemented using dense-storage so the interface only includes the corresponding dense-storage BLAS functions. The full BLAS functionality for band-format and packed-format matrices is available through the low-level CBLAS interface. Similarly, GSL vectors are restricted to positive strides, whereas the low-level CBLAS interface supports negative strides as specified in the BLAS standard 1.
The interface for the gsl_cblas layer is specified in the file
gsl_cblas.h. This interface corresponds to the BLAS Technical
Forum’s standard for the C interface to legacy BLAS
implementations. Users who have access to other conforming CBLAS
implementations can use these in place of the version provided by the
library. Note that users who have only a Fortran BLAS library can
use a CBLAS conformant wrapper to convert it into a CBLAS
library. A reference CBLAS wrapper for legacy Fortran
implementations exists as part of the CBLAS standard and can
be obtained from Netlib. The complete set of CBLAS functions is
listed in an appendix.
There are three levels of BLAS operations,
Level 1 |
Vector operations, e.g. |
Level 2 |
Matrix-vector operations, e.g. |
Level 3 |
Matrix-matrix operations, e.g. |
Each routine has a name which specifies the operation, the type of matrices involved and their precisions. Some of the most common operations and their names are given below,
DOT |
scalar product, |
AXPY |
vector sum, |
MV |
matrix-vector product, |
SV |
matrix-vector solve, |
MM |
matrix-matrix product, |
SM |
matrix-matrix solve, |
The types of matrices are,
GE |
general |
GB |
general band |
SY |
symmetric |
SB |
symmetric band |
SP |
symmetric packed |
HE |
hermitian |
HB |
hermitian band |
HP |
hermitian packed |
TR |
triangular |
TB |
triangular band |
TP |
triangular packed |
Each operation is defined for four precisions,
S |
single real |
D |
double real |
C |
single complex |
Z |
double complex |
Thus, for example, the name SGEMM stands for “single-precision general matrix-matrix multiply” and ZGEMM stands for “double-precision complex matrix-matrix multiply”.
Note that the vector and matrix arguments to BLAS functions must not be aliased, as the results are undefined when the underlying arrays overlap (Aliasing of arrays).
GSL BLAS Interface¶
GSL provides dense vector and matrix objects, based on the relevant
built-in types. The library provides an interface to the BLAS
operations which apply to these objects. The interface to this
functionality is given in the file gsl_blas.h.
Level 1¶
-
int gsl_blas_sdsdot(float alpha, const gsl_vector_float *x, const gsl_vector_float *y, float *result)¶
This function computes the sum
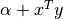 for the vectors
for the vectors
xandy, returning the result inresult.
-
int gsl_blas_sdot(const gsl_vector_float *x, const gsl_vector_float *y, float *result)¶
-
int gsl_blas_dsdot(const gsl_vector_float *x, const gsl_vector_float *y, double *result)¶
-
int gsl_blas_ddot(const gsl_vector *x, const gsl_vector *y, double *result)¶
These functions compute the scalar product
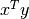 for the vectors
for the vectors
xandy, returning the result inresult.
-
int gsl_blas_cdotu(const gsl_vector_complex_float *x, const gsl_vector_complex_float *y, gsl_complex_float *dotu)¶
-
int gsl_blas_zdotu(const gsl_vector_complex *x, const gsl_vector_complex *y, gsl_complex *dotu)¶
These functions compute the complex scalar product
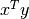 for the
vectors
for the
vectors xandy, returning the result indotu
-
int gsl_blas_cdotc(const gsl_vector_complex_float *x, const gsl_vector_complex_float *y, gsl_complex_float *dotc)¶
-
int gsl_blas_zdotc(const gsl_vector_complex *x, const gsl_vector_complex *y, gsl_complex *dotc)¶
These functions compute the complex conjugate scalar product
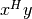 for the vectors
for the vectors xandy, returning the result indotc
-
float gsl_blas_snrm2(const gsl_vector_float *x)¶
-
double gsl_blas_dnrm2(const gsl_vector *x)¶
These functions compute the Euclidean norm
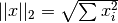 of the vector
of the vector x.
-
float gsl_blas_scnrm2(const gsl_vector_complex_float *x)¶
-
double gsl_blas_dznrm2(const gsl_vector_complex *x)¶
These functions compute the Euclidean norm of the complex vector
x,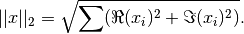
-
float gsl_blas_sasum(const gsl_vector_float *x)¶
-
double gsl_blas_dasum(const gsl_vector *x)¶
These functions compute the absolute sum
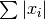 of the
elements of the vector
of the
elements of the vector x.
-
float gsl_blas_scasum(const gsl_vector_complex_float *x)¶
-
double gsl_blas_dzasum(const gsl_vector_complex *x)¶
These functions compute the sum of the magnitudes of the real and imaginary parts of the complex vector
x,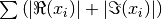 .
.
-
CBLAS_INDEX_t gsl_blas_isamax(const gsl_vector_float *x)¶
-
CBLAS_INDEX_t gsl_blas_idamax(const gsl_vector *x)¶
-
CBLAS_INDEX_t gsl_blas_icamax(const gsl_vector_complex_float *x)¶
-
CBLAS_INDEX_t gsl_blas_izamax(const gsl_vector_complex *x)¶
These functions return the index of the largest element of the vector
x. The largest element is determined by its absolute magnitude for real vectors and by the sum of the magnitudes of the real and imaginary parts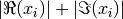 for complex vectors. If the
largest value occurs several times then the index of the first
occurrence is returned.
for complex vectors. If the
largest value occurs several times then the index of the first
occurrence is returned.
-
int gsl_blas_sswap(gsl_vector_float *x, gsl_vector_float *y)¶
-
int gsl_blas_dswap(gsl_vector *x, gsl_vector *y)¶
-
int gsl_blas_cswap(gsl_vector_complex_float *x, gsl_vector_complex_float *y)¶
-
int gsl_blas_zswap(gsl_vector_complex *x, gsl_vector_complex *y)¶
These functions exchange the elements of the vectors
xandy.
-
int gsl_blas_scopy(const gsl_vector_float *x, gsl_vector_float *y)¶
-
int gsl_blas_dcopy(const gsl_vector *x, gsl_vector *y)¶
-
int gsl_blas_ccopy(const gsl_vector_complex_float *x, gsl_vector_complex_float *y)¶
-
int gsl_blas_zcopy(const gsl_vector_complex *x, gsl_vector_complex *y)¶
These functions copy the elements of the vector
xinto the vectory.
-
int gsl_blas_saxpy(float alpha, const gsl_vector_float *x, gsl_vector_float *y)¶
-
int gsl_blas_daxpy(double alpha, const gsl_vector *x, gsl_vector *y)¶
-
int gsl_blas_caxpy(const gsl_complex_float alpha, const gsl_vector_complex_float *x, gsl_vector_complex_float *y)¶
-
int gsl_blas_zaxpy(const gsl_complex alpha, const gsl_vector_complex *x, gsl_vector_complex *y)¶
-
void gsl_blas_sscal(float alpha, gsl_vector_float *x)¶
-
void gsl_blas_dscal(double alpha, gsl_vector *x)¶
-
void gsl_blas_cscal(const gsl_complex_float alpha, gsl_vector_complex_float *x)¶
-
void gsl_blas_zscal(const gsl_complex alpha, gsl_vector_complex *x)¶
-
void gsl_blas_csscal(float alpha, gsl_vector_complex_float *x)¶
-
void gsl_blas_zdscal(double alpha, gsl_vector_complex *x)¶
These functions rescale the vector
xby the multiplicative factoralpha.
-
int gsl_blas_srotg(float a[], float b[], float c[], float s[])¶
-
int gsl_blas_drotg(double a[], double b[], double c[], double s[])¶
These functions compute a Givens rotation
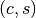 which zeroes the
vector
which zeroes the
vector 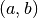 ,
,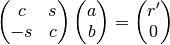
-
int gsl_blas_srot(gsl_vector_float *x, gsl_vector_float *y, float c, float s)¶
-
int gsl_blas_drot(gsl_vector *x, gsl_vector *y, const double c, const double s)¶
These functions apply a Givens rotation
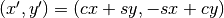 to the vectors
to the vectors x,y.
-
int gsl_blas_srotmg(float d1[], float d2[], float b1[], float b2, float P[])¶
-
int gsl_blas_drotmg(double d1[], double d2[], double b1[], double b2, double P[])¶
These functions compute a modified Givens transformation. The modified Givens transformation is defined in the original Level-1 BLAS specification, given in the references.
-
int gsl_blas_srotm(gsl_vector_float *x, gsl_vector_float *y, const float P[])¶
-
int gsl_blas_drotm(gsl_vector *x, gsl_vector *y, const double P[])¶
These functions apply a modified Givens transformation.
Level 2¶
-
int gsl_blas_sgemv(CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, float alpha, const gsl_matrix_float *A, const gsl_vector_float *x, float beta, gsl_vector_float *y)¶
-
int gsl_blas_dgemv(CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, double alpha, const gsl_matrix *A, const gsl_vector *x, double beta, gsl_vector *y)¶
-
int gsl_blas_cgemv(CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, const gsl_complex_float alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex_float *A, const gsl_vector_complex_float *x, const gsl_complex_float beta, gsl_vector_complex_float *y)¶
-
int gsl_blas_zgemv(CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, const gsl_complex alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex *A, const gsl_vector_complex *x, const gsl_complex beta, gsl_vector_complex *y)¶
These functions compute the matrix-vector product and sum
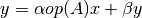 ,
where
,
where 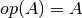 ,
, 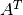 ,
, 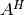 for
for TransA=CblasNoTrans,CblasTrans,CblasConjTrans.
-
int gsl_blas_strmv(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_DIAG_t Diag, const gsl_matrix_float *A, gsl_vector_float *x)¶
-
int gsl_blas_dtrmv(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_DIAG_t Diag, const gsl_matrix *A, gsl_vector *x)¶
-
int gsl_blas_ctrmv(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_DIAG_t Diag, const gsl_matrix_complex_float *A, gsl_vector_complex_float *x)¶
-
int gsl_blas_ztrmv(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_DIAG_t Diag, const gsl_matrix_complex *A, gsl_vector_complex *x)¶
These functions compute the matrix-vector product
 for the triangular matrix
for the triangular matrix A, where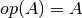 ,
, 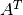 ,
, 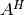 for
for TransA=CblasNoTrans,CblasTrans,CblasConjTrans. WhenUploisCblasUpperthen the upper triangle ofAis used, and whenUploisCblasLowerthen the lower triangle ofAis used. IfDiagisCblasNonUnitthen the diagonal of the matrix is used, but ifDiagisCblasUnitthen the diagonal elements of the matrixAare taken as unity and are not referenced.
-
int gsl_blas_strsv(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_DIAG_t Diag, const gsl_matrix_float *A, gsl_vector_float *x)¶
-
int gsl_blas_dtrsv(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_DIAG_t Diag, const gsl_matrix *A, gsl_vector *x)¶
-
int gsl_blas_ctrsv(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_DIAG_t Diag, const gsl_matrix_complex_float *A, gsl_vector_complex_float *x)¶
-
int gsl_blas_ztrsv(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_DIAG_t Diag, const gsl_matrix_complex *A, gsl_vector_complex *x)¶
These functions compute
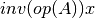 for
for x, where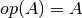 ,
, 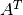 ,
, 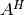 for
for TransA=CblasNoTrans,CblasTrans,CblasConjTrans. WhenUploisCblasUpperthen the upper triangle ofAis used, and whenUploisCblasLowerthen the lower triangle ofAis used. IfDiagisCblasNonUnitthen the diagonal of the matrix is used, but ifDiagisCblasUnitthen the diagonal elements of the matrixAare taken as unity and are not referenced.
-
int gsl_blas_ssymv(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, float alpha, const gsl_matrix_float *A, const gsl_vector_float *x, float beta, gsl_vector_float *y)¶
-
int gsl_blas_dsymv(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, double alpha, const gsl_matrix *A, const gsl_vector *x, double beta, gsl_vector *y)¶
These functions compute the matrix-vector product and sum
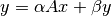 for the symmetric matrix
for the symmetric matrix A. Since the matrixAis symmetric only its upper half or lower half need to be stored. WhenUploisCblasUpperthen the upper triangle and diagonal ofAare used, and whenUploisCblasLowerthen the lower triangle and diagonal ofAare used.
-
int gsl_blas_chemv(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, const gsl_complex_float alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex_float *A, const gsl_vector_complex_float *x, const gsl_complex_float beta, gsl_vector_complex_float *y)¶
-
int gsl_blas_zhemv(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, const gsl_complex alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex *A, const gsl_vector_complex *x, const gsl_complex beta, gsl_vector_complex *y)¶
These functions compute the matrix-vector product and sum
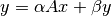 for the hermitian matrix
for the hermitian matrix A. Since the matrixAis hermitian only its upper half or lower half need to be stored. WhenUploisCblasUpperthen the upper triangle and diagonal ofAare used, and whenUploisCblasLowerthen the lower triangle and diagonal ofAare used. The imaginary elements of the diagonal are automatically assumed to be zero and are not referenced.
-
int gsl_blas_sger(float alpha, const gsl_vector_float *x, const gsl_vector_float *y, gsl_matrix_float *A)¶
-
int gsl_blas_dger(double alpha, const gsl_vector *x, const gsl_vector *y, gsl_matrix *A)¶
-
int gsl_blas_cgeru(const gsl_complex_float alpha, const gsl_vector_complex_float *x, const gsl_vector_complex_float *y, gsl_matrix_complex_float *A)¶
-
int gsl_blas_zgeru(const gsl_complex alpha, const gsl_vector_complex *x, const gsl_vector_complex *y, gsl_matrix_complex *A)¶
These functions compute the rank-1 update
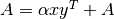 of
the matrix
of
the matrix A.
-
int gsl_blas_cgerc(const gsl_complex_float alpha, const gsl_vector_complex_float *x, const gsl_vector_complex_float *y, gsl_matrix_complex_float *A)¶
-
int gsl_blas_zgerc(const gsl_complex alpha, const gsl_vector_complex *x, const gsl_vector_complex *y, gsl_matrix_complex *A)¶
These functions compute the conjugate rank-1 update
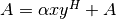 of the matrix
of the matrix A.
-
int gsl_blas_ssyr(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, float alpha, const gsl_vector_float *x, gsl_matrix_float *A)¶
-
int gsl_blas_dsyr(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, double alpha, const gsl_vector *x, gsl_matrix *A)¶
These functions compute the symmetric rank-1 update
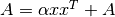 of the symmetric matrix
of the symmetric matrix A. Since the matrixAis symmetric only its upper half or lower half need to be stored. WhenUploisCblasUpperthen the upper triangle and diagonal ofAare used, and whenUploisCblasLowerthen the lower triangle and diagonal ofAare used.
-
int gsl_blas_cher(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, float alpha, const gsl_vector_complex_float *x, gsl_matrix_complex_float *A)¶
-
int gsl_blas_zher(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, double alpha, const gsl_vector_complex *x, gsl_matrix_complex *A)¶
These functions compute the hermitian rank-1 update
 of the hermitian matrix
of the hermitian matrix A. Since the matrixAis hermitian only its upper half or lower half need to be stored. WhenUploisCblasUpperthen the upper triangle and diagonal ofAare used, and whenUploisCblasLowerthen the lower triangle and diagonal ofAare used. The imaginary elements of the diagonal are automatically set to zero.
-
int gsl_blas_ssyr2(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, float alpha, const gsl_vector_float *x, const gsl_vector_float *y, gsl_matrix_float *A)¶
-
int gsl_blas_dsyr2(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, double alpha, const gsl_vector *x, const gsl_vector *y, gsl_matrix *A)¶
These functions compute the symmetric rank-2 update
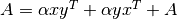 of the symmetric matrix
of the symmetric matrix A. Since the matrixAis symmetric only its upper half or lower half need to be stored. WhenUploisCblasUpperthen the upper triangle and diagonal ofAare used, and whenUploisCblasLowerthen the lower triangle and diagonal ofAare used.
-
int gsl_blas_cher2(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, const gsl_complex_float alpha, const gsl_vector_complex_float *x, const gsl_vector_complex_float *y, gsl_matrix_complex_float *A)¶
-
int gsl_blas_zher2(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, const gsl_complex alpha, const gsl_vector_complex *x, const gsl_vector_complex *y, gsl_matrix_complex *A)¶
These functions compute the hermitian rank-2 update
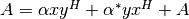 of the hermitian matrix
of the hermitian matrix A. Since the matrixAis hermitian only its upper half or lower half need to be stored. WhenUploisCblasUpperthen the upper triangle and diagonal ofAare used, and whenUploisCblasLowerthen the lower triangle and diagonal ofAare used. The imaginary elements of the diagonal are automatically set to zero.
Level 3¶
-
int gsl_blas_sgemm(CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransB, float alpha, const gsl_matrix_float *A, const gsl_matrix_float *B, float beta, gsl_matrix_float *C)¶
-
int gsl_blas_dgemm(CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransB, double alpha, const gsl_matrix *A, const gsl_matrix *B, double beta, gsl_matrix *C)¶
-
int gsl_blas_cgemm(CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransB, const gsl_complex_float alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex_float *A, const gsl_matrix_complex_float *B, const gsl_complex_float beta, gsl_matrix_complex_float *C)¶
-
int gsl_blas_zgemm(CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransB, const gsl_complex alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex *A, const gsl_matrix_complex *B, const gsl_complex beta, gsl_matrix_complex *C)¶
These functions compute the matrix-matrix product and sum
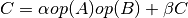 where
where 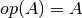 ,
, 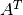 ,
,
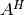 for
for TransA=CblasNoTrans,CblasTrans,CblasConjTransand similarly for the parameterTransB.
-
int gsl_blas_ssymm(CBLAS_SIDE_t Side, CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, float alpha, const gsl_matrix_float *A, const gsl_matrix_float *B, float beta, gsl_matrix_float *C)¶
-
int gsl_blas_dsymm(CBLAS_SIDE_t Side, CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, double alpha, const gsl_matrix *A, const gsl_matrix *B, double beta, gsl_matrix *C)¶
-
int gsl_blas_csymm(CBLAS_SIDE_t Side, CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, const gsl_complex_float alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex_float *A, const gsl_matrix_complex_float *B, const gsl_complex_float beta, gsl_matrix_complex_float *C)¶
-
int gsl_blas_zsymm(CBLAS_SIDE_t Side, CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, const gsl_complex alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex *A, const gsl_matrix_complex *B, const gsl_complex beta, gsl_matrix_complex *C)¶
These functions compute the matrix-matrix product and sum
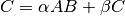 for
for SideisCblasLeftand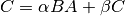 for
for SideisCblasRight, where the matrixAis symmetric. WhenUploisCblasUpperthen the upper triangle and diagonal ofAare used, and whenUploisCblasLowerthen the lower triangle and diagonal ofAare used.
-
int gsl_blas_chemm(CBLAS_SIDE_t Side, CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, const gsl_complex_float alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex_float *A, const gsl_matrix_complex_float *B, const gsl_complex_float beta, gsl_matrix_complex_float *C)¶
-
int gsl_blas_zhemm(CBLAS_SIDE_t Side, CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, const gsl_complex alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex *A, const gsl_matrix_complex *B, const gsl_complex beta, gsl_matrix_complex *C)¶
These functions compute the matrix-matrix product and sum
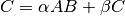 for
for SideisCblasLeftand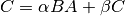 for
for SideisCblasRight, where the matrixAis hermitian. WhenUploisCblasUpperthen the upper triangle and diagonal ofAare used, and whenUploisCblasLowerthen the lower triangle and diagonal ofAare used. The imaginary elements of the diagonal are automatically set to zero.
-
int gsl_blas_strmm(CBLAS_SIDE_t Side, CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_DIAG_t Diag, float alpha, const gsl_matrix_float *A, gsl_matrix_float *B)¶
-
int gsl_blas_dtrmm(CBLAS_SIDE_t Side, CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_DIAG_t Diag, double alpha, const gsl_matrix *A, gsl_matrix *B)¶
-
int gsl_blas_ctrmm(CBLAS_SIDE_t Side, CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_DIAG_t Diag, const gsl_complex_float alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex_float *A, gsl_matrix_complex_float *B)¶
-
int gsl_blas_ztrmm(CBLAS_SIDE_t Side, CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_DIAG_t Diag, const gsl_complex alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex *A, gsl_matrix_complex *B)¶
These functions compute the matrix-matrix product
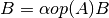 for
for SideisCblasLeftand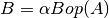 for
for
SideisCblasRight. The matrixAis triangular and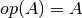 ,
, 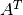 ,
, 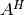 for
for TransA=CblasNoTrans,CblasTrans,CblasConjTrans. WhenUploisCblasUpperthen the upper triangle ofAis used, and whenUploisCblasLowerthen the lower triangle ofAis used. IfDiagisCblasNonUnitthen the diagonal ofAis used, but ifDiagisCblasUnitthen the diagonal elements of the matrixAare taken as unity and are not referenced.
-
int gsl_blas_strsm(CBLAS_SIDE_t Side, CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_DIAG_t Diag, float alpha, const gsl_matrix_float *A, gsl_matrix_float *B)¶
-
int gsl_blas_dtrsm(CBLAS_SIDE_t Side, CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_DIAG_t Diag, double alpha, const gsl_matrix *A, gsl_matrix *B)¶
-
int gsl_blas_ctrsm(CBLAS_SIDE_t Side, CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_DIAG_t Diag, const gsl_complex_float alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex_float *A, gsl_matrix_complex_float *B)¶
-
int gsl_blas_ztrsm(CBLAS_SIDE_t Side, CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t TransA, CBLAS_DIAG_t Diag, const gsl_complex alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex *A, gsl_matrix_complex *B)¶
These functions compute the inverse-matrix matrix product
 for
for SideisCblasLeftand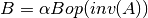 for
for
SideisCblasRight. The matrixAis triangular and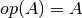 ,
, 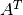 ,
, 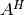 for
for TransA=CblasNoTrans,CblasTrans,CblasConjTrans. WhenUploisCblasUpperthen the upper triangle ofAis used, and whenUploisCblasLowerthen the lower triangle ofAis used. IfDiagisCblasNonUnitthen the diagonal ofAis used, but ifDiagisCblasUnitthen the diagonal elements of the matrixAare taken as unity and are not referenced.
-
int gsl_blas_ssyrk(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t Trans, float alpha, const gsl_matrix_float *A, float beta, gsl_matrix_float *C)¶
-
int gsl_blas_dsyrk(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t Trans, double alpha, const gsl_matrix *A, double beta, gsl_matrix *C)¶
-
int gsl_blas_csyrk(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t Trans, const gsl_complex_float alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex_float *A, const gsl_complex_float beta, gsl_matrix_complex_float *C)¶
-
int gsl_blas_zsyrk(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t Trans, const gsl_complex alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex *A, const gsl_complex beta, gsl_matrix_complex *C)¶
These functions compute a rank-k update of the symmetric matrix
C,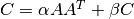 when
when TransisCblasNoTransand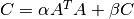 when
when
TransisCblasTrans. Since the matrixCis symmetric only its upper half or lower half need to be stored. WhenUploisCblasUpperthen the upper triangle and diagonal ofCare used, and whenUploisCblasLowerthen the lower triangle and diagonal ofCare used.
-
int gsl_blas_cherk(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t Trans, float alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex_float *A, float beta, gsl_matrix_complex_float *C)¶
-
int gsl_blas_zherk(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t Trans, double alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex *A, double beta, gsl_matrix_complex *C)¶
These functions compute a rank-k update of the hermitian matrix
C,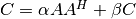 when
when TransisCblasNoTransand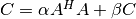 when
when
TransisCblasConjTrans. Since the matrixCis hermitian only its upper half or lower half need to be stored. WhenUploisCblasUpperthen the upper triangle and diagonal ofCare used, and whenUploisCblasLowerthen the lower triangle and diagonal ofCare used. The imaginary elements of the diagonal are automatically set to zero.
-
int gsl_blas_ssyr2k(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t Trans, float alpha, const gsl_matrix_float *A, const gsl_matrix_float *B, float beta, gsl_matrix_float *C)¶
-
int gsl_blas_dsyr2k(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t Trans, double alpha, const gsl_matrix *A, const gsl_matrix *B, double beta, gsl_matrix *C)¶
-
int gsl_blas_csyr2k(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t Trans, const gsl_complex_float alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex_float *A, const gsl_matrix_complex_float *B, const gsl_complex_float beta, gsl_matrix_complex_float *C)¶
-
int gsl_blas_zsyr2k(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t Trans, const gsl_complex alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex *A, const gsl_matrix_complex *B, const gsl_complex beta, gsl_matrix_complex *C)¶
These functions compute a rank-2k update of the symmetric matrix
C,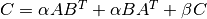 when
when TransisCblasNoTransand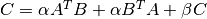 when
when
TransisCblasTrans. Since the matrixCis symmetric only its upper half or lower half need to be stored. WhenUploisCblasUpperthen the upper triangle and diagonal ofCare used, and whenUploisCblasLowerthen the lower triangle and diagonal ofCare used.
-
int gsl_blas_cher2k(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t Trans, const gsl_complex_float alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex_float *A, const gsl_matrix_complex_float *B, float beta, gsl_matrix_complex_float *C)¶
-
int gsl_blas_zher2k(CBLAS_UPLO_t Uplo, CBLAS_TRANSPOSE_t Trans, const gsl_complex alpha, const gsl_matrix_complex *A, const gsl_matrix_complex *B, double beta, gsl_matrix_complex *C)¶
These functions compute a rank-2k update of the hermitian matrix
C,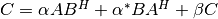 when
when TransisCblasNoTransand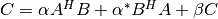 when
when
TransisCblasConjTrans. Since the matrixCis hermitian only its upper half or lower half need to be stored. WhenUploisCblasUpperthen the upper triangle and diagonal ofCare used, and whenUploisCblasLowerthen the lower triangle and diagonal ofCare used. The imaginary elements of the diagonal are automatically set to zero.
Examples¶
The following program computes the product of two matrices using the Level-3 BLAS function DGEMM,
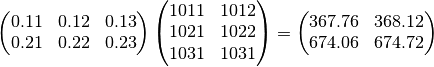
The matrices are stored in row major order, according to the C convention for arrays.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <gsl/gsl_blas.h>
int
main (void)
{
double a[] = { 0.11, 0.12, 0.13,
0.21, 0.22, 0.23 };
double b[] = { 1011, 1012,
1021, 1022,
1031, 1032 };
double c[] = { 0.00, 0.00,
0.00, 0.00 };
gsl_matrix_view A = gsl_matrix_view_array(a, 2, 3);
gsl_matrix_view B = gsl_matrix_view_array(b, 3, 2);
gsl_matrix_view C = gsl_matrix_view_array(c, 2, 2);
/* Compute C = A B */
gsl_blas_dgemm (CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans,
1.0, &A.matrix, &B.matrix,
0.0, &C.matrix);
printf ("[ %g, %g\n", c[0], c[1]);
printf (" %g, %g ]\n", c[2], c[3]);
return 0;
}
Here is the output from the program,
[ 367.76, 368.12
674.06, 674.72 ]
References and Further Reading¶
Information on the BLAS standards, including both the legacy and updated interface standards, is available online from the BLAS Homepage and BLAS Technical Forum web-site.
BLAS Homepage, http://www.netlib.org/blas/
BLAS Technical Forum, http://www.netlib.org/blas/blast-forum/
The following papers contain the specifications for Level 1, Level 2 and Level 3 BLAS.
C. Lawson, R. Hanson, D. Kincaid, F. Krogh, “Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms for Fortran Usage”, ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, Vol.: 5 (1979), Pages 308–325.
J.J. Dongarra, J. DuCroz, S. Hammarling, R. Hanson, “An Extended Set of Fortran Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms”, ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, Vol.: 14, No.: 1 (1988), Pages 1–32.
J.J. Dongarra, I. Duff, J. DuCroz, S. Hammarling, “A Set of Level 3 Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms”, ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, Vol.: 16 (1990), Pages 1–28.
Postscript versions of the latter two papers are available from http://www.netlib.org/blas/. A CBLAS wrapper for Fortran BLAS libraries is available from the same location.
Footnotes
- 1
In the low-level CBLAS interface, a negative stride accesses the vector elements in reverse order, i.e. the
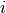 -th element is given by
-th element is given by
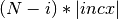 for
for 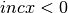 .
.